
Why Japan is so Advanced: Top 9 Reasons
If you believe the media and TV, Japan appears to be a country straight from the future. Considering technological innovation and socio-economic structure, Japan appears to be way ahead of most western countries. Is it actually a technological wonderland as it seems to be?
Japan is an advanced country, not only in terms of technology but society as a whole. They have everything from super-fast bullet trains to talking toilets and robots. An overwhelming number of vending machines are there that contain everything, even clothes and shoes. These advancements can be seen as the results of the modern mind of Japanese people whose insatiable hunger for progressiveness has made Japan that it is today.
Quick Navigation

Japan’s Advancement: When the Movement Started?
Not every nation can take lessons from their historical mistakes. Japan is not one of them. It’s today’s standing as an advanced nation is the result of the pre-WWII modernization efforts.
In fact, the process had started almost 100 years before WWII. Its goal to be on an equal footing with any European power in terms of technological progress started from the Meiji Restoration in 1868.
The shogunate of Japan (military dictatorship from 1192 to 1867) had shut the country off from the outside world since the mid-1600s. It was an attempt to keep the country unaffected by the ideological shift in the Western world.

That solitary state lasted until 1853 before Americans invaded the country with a fleet of heavily-armed ships and forced the Japanese ruler to establish contact with the rest of the world.
When the country opened its door for others, new and innovative concepts and ideas flooded the country and inspired the people to embark on their creative journeys. The Meiji Emperor was on the lead toward that boom in the sectors of technology and industries.
Despite being on the losing side in WWII, Japan did not face any economic disaster, thanks to a treaty with the United States and the government’s solid plans.
Below are the top reasons behind Japan’s prosperous and technologically advanced status.
State Patronizing Capitalism
State-funded industrial capitalism created a sustainable environment for industries to flourish. The government had a firm hold on the companies and assisted them to work on new, innovative projects.
The main focus was on the electronics sector, not only on the end products but also on the engineering and technology behind those products. Computers and semiconductors were a major part of that electronic revolution.
Glenn R. Fong wrote in his research paper that the government assistance had improved the overall condition of the industries. There were trade protection, tax benefits, and sufficient subsidies for research and development.
The execution of this kind of capitalism was highly influential and successful. Japanese companies could borrow money from the government at an incredibly low-interest rate and were eligible to take more loans if they could just cover the repayments. It helped them to focus on growth rather than making profits.

Japan focused on building the economy around domestic industrialization, so they took some specific actions:
- Exploiting the domestic and international prices for electronic goods to attract Western buyers.
- In the domestic market, increasing trade barriers against similar goods.
- Shifting the industrial priorities to less expensive products, unlike the USA that had literally poured money into aerospace and weapons systems.
The Influences of Family-Owned Businesses
Even before WWII, Japan had patronizers for heavy industry in the form of the zaibatsu (財閥, “financial clique”) or family-owned business conglomerates. Many of these corporations or their employees switched their track in the 1960s and 1970s in the favor of high-tech electronic products.
If you look at the history of Japanese giant electronics companies, you will understand this shift of paradigm during that time. The most popular example is Toyota, the giant Japanese automotive company.

It was founded as a cloth loom manufacturing company in the 1800s. It got into the car business in the 1920s and became one of the biggest car companies in the world. Similarly, take the instances of famous electronics companies Panasonic, Sharp, Nintendo, and Toshiba. None of these started as what they are today.
As discussed above, the government also got involved through the Ministry of International Trade and Industry (MITI) and played an active role in managing industrial production.
STEM-Based Curriculum in the Universities
The systematic push toward creating an advanced nation came from everywhere, including educational institutes too. Many Japanese universities started as technical schools to produce as many STEM (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics) majors as possible.
Those young graduates had a major contribution to the development of the country. They have always been and still are showing great performance in mathematics and science among 37 OECD (Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development) member countries.
One of the reasons for this success was the government’s spending a substantial percentage of the GDP on education. According to an OECD survey, Japanese adults have the highest level of literacy and numeracy among those of other participating countries.

Female literacy is also significantly higher than in many other countries. With that impressive percentage, Japan ranks 10th in the application of that proficiency for solving problems in technical environments.
Compared to the neighboring country China, Japanese people are way advanced in terms of education and being familiar with the technology. While 95% of Japanese students complete their high school graduation, it’s less than 84% in China. Similarly, 93.3% of Japanese use technology while it’s lower than 53.1% in China.
Japan also boasts some of the best universities in the world. The quality of education is another catalyst in the burgeoning industrial and technological progress.
Steady Funding for Scientific Research
In the 150 years after the Meiji Restoration, Japan’s journey toward modernization included huge funding for scientific research. It was one of the key driving forces behind Japan being so advanced these days.
All the research money has produced extensive progress in computer science, robotics, and natural science. The country has produced many Nobel Laureates, and the number is definitely higher than any other Asian country.
Since 2000, this spending on technology research has declined compared to the previous time and other countries like South Korea and China. It declined in the case of both educational institutes and public and nonprofit organizations.

However, Japan still spends a lump sum of money for research purposes compared to many other countries. The Promotion of Science (JSPS) has been active since 1932 for the development of social sciences, natural sciences, and humanities. This institution became independent in 2003 for better assisting particular educational entities and researchers.
The JSPS oversees many initiatives, such as the Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (KAKENHI) program, which provides funds for research across all scientific fields. The funds that KEKENHI distributes each year make up half of the country’s competitive research funding.
The Demise of Military Power
After the defense treaty (Treaty of Mutual Cooperation and Security) with the United States in 1960, the Japanese army was officially disbanded. The forced demobilization and ban on rearmament caused much of their defense to fizzle out but it was highly rewarding in a different way.

The government was able to save a fortune on that it had to spend on the military otherwise. Such a huge amount of money played a crucial role in growing the country’s economy and building the nation in the post-war era.
American Patronization
The defense treaty created an opening for Japanese goods in the American market. With investments coming from the USA, the Ministry of International Trade and Industry (MITI) took effective measurements to create the Japanese market share in the USA.
Japanese companies also came forward with a huge amount of money that went into building infrastructures and developing heavy industries. Such an early setup helped Japan to be in a highly advantageous position when American consumers started showing a growing interest in electronics.

At the initial stage, Japanese electric goods were quite unreliable and cheap, just like the Chinese products these days. But they bounced back with their innovativeness and consistent improvement of the existing gadgets. For example, they transformed the clunky, slow fax machine into a compact, faster unit, and thereby pocketing the lion’s share of the fax machine sales.
Japanese electronic brands like Panasonic, Sony, and Nintendo soon became household names because they had started producing high-quality and reliable products.
The acceptance of Japanese tech products in the American market boosted the Japanese economy at both macro and micro levels. The American government provided resources and eased the intricate rules of export and import for Japanese companies. It helped them to create a strong foothold in the USA market.

It can be said that the American government implemented some policies that made an opening for the Japanese companies, which they used fully to develop a world-class economy in their own country.
Clever Utilization of Nuclear Energy
There’s no doubt that nuclear energy plays a large part in determining a country’s position in the field of world power. Japan’s strive to reduce the dependency on imported fuel started in 1973. By 2008, the country had 55 nuclear reactors, generating around 34.5% of the country’s electricity.
The 2011 disaster at the Fukushima I Nuclear Power Plant brought a temporary halt to this initiative as the government permanently shut down 20 nuclear reactors. But the country is on the track of regaining the previous energy production.
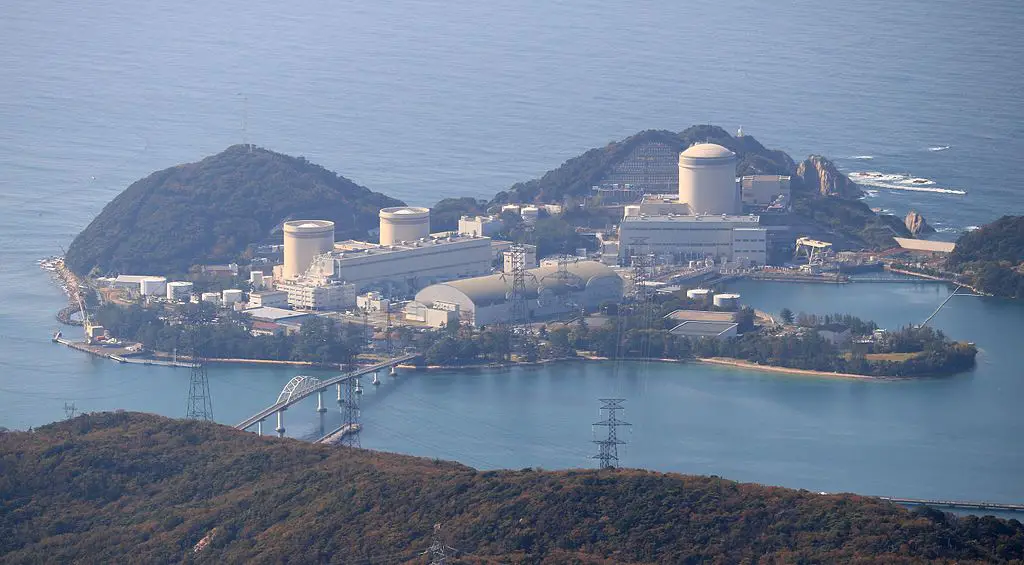

The country has a long-term energy policy in place with plans to cover around 20 to 22 percent of total electricity generation from nuclear energy by 2030. With that policy in mind, the government is working on to start operation in the still-functioning reactors.
Of the 34 functioning units, 9 are currently fully operational. The Nuclear Regulation Authority (NRA) has approved another 6 reactors and kept 12 more under review. It seems that the remaining 9 units will undergo the same process in the next couple of years. Check a chart of the country’s capacity of generating nuclear electricity here.
An Up-to-date Space Program
Many First-World countries have a space program in place that has become indicative of how progressive a nation is. Japan also has one in place, which started its journey after WWII.
A University of Tokyo professor established the Japanese space program in the mid-1950s. In the next couple of decades, there were several organizations developing rockets and satellites and doing aviation research. All of them merged into the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) in 2003.

Japan has been an active partner of the USA’s space program for more than 40 years. It also signed on the International Space Station program in the 1980s after a hiatus in the 1970s. It has recently joined NASA’s latest moon-related program, Artemis. Also, it’s important to mention that the JAXA has sent 12 astronauts in space since 1990.
The JAXA has been involved in many successful initiatives. By collaborating with Mitsubishi, it has built the H-IIA rocket that yielded many fruitful scientific missions. Some other successful ventures are the HALCA satellite, Hayabusa robotic spacecraft, Hayabusa2, and an experimental spacecraft named IKAROS.
Development of Cutting-Edge Technology
It’s not surprising that Japan’s revolution in the electronics sector was meant to lead the country toward something big. In the field of electronics and technology, Japan has delivered some groundbreaking progress and scores of unique innovations.
Everyone may remember those good old Nintendo games and Sony Walkman but the 21st-century Japanese inventions are more about improving the ways of life rather than just being means of entertainment.
Some mind-blowing Japanese technological inventions that show the glimpse of predicted the future are:
Robots and AI
One reason for Japan’s current advancement is its success in robotics. It has almost 300,000 robots working in the industrial sector, the largest number by any means in any country in the world.
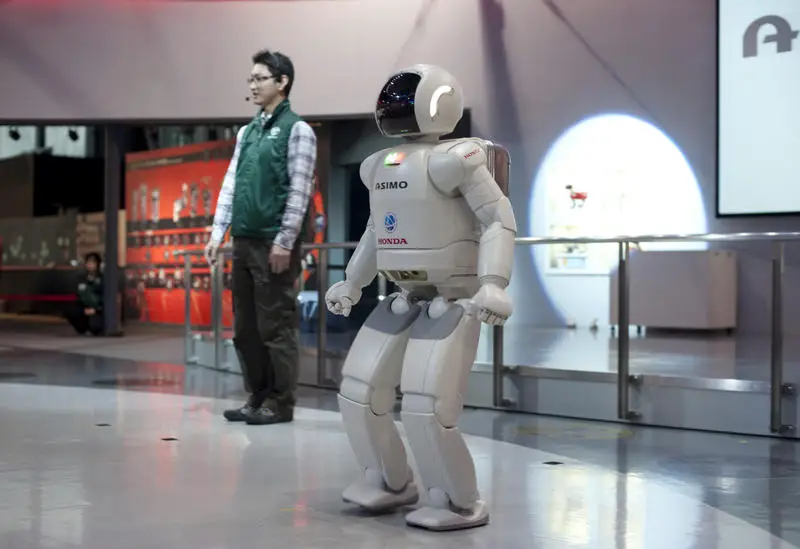

One significant instance of using robots is sending one to decontaminate the Fukushima power plant. The country is also heading toward starting robotic surgery, which will definitely be a groundbreaking innovation in the field of medicine.
High-Speed Trains
Japan’s Shinkansen (bullet train) is world-famous. Operating since 1964, the trains offer style, comfort, and speed that fit in a futuristic environment.
Currently, these bullet trains can reach up to 320km/h, thanks to the use of maglev technology that creates a zero-resistance transportation path for the train carriages. Because of the country’s impressive success in semiconductor technology, there is a great chance that the speed of these trains can be increased to over 600km/h.
Batteries
Japan is way ahead than other countries when it comes to developing high-tech batteries. Japanese engineer Akira Yoshino received the Nobel Prize in 2019 for his remarkable contribution in developing lithium-ion batteries. The company Yoshino works for has already developed an all-solid-state battery unit that can hold the charge longer than any other battery cell currently available.
Microscopic Circuits
South Korea, China, and the USA take the top spots when it comes to mobile phones but the world tech sectors cannot function without Japanese parts and equipment.
No one can beat Japanese companies in the production of high-quality, fast microscopic circuits because of their advanced technical knowledge and getting access to the most purified silicon in the world.
The Cells Alive System (C.A.S.)
A Japanese company, ABI Corporation, has developed a line of commercial freezers that keep intact the freshness of food for a longer time. It prevents the formation of ice crystals, which are the culprit in ruining the food texture and taste, by creating an electrical field. The process spins the water particles to prevent them from becoming crystals and reduces oxidation by 98% compared to a regular freezer.
These freezers work five times faster than conventional freezers for freezing food but consume 30% less power. If the technology takes off, it will provide a remarkable contribution to organ transplantation fields, organ banking, and the food industry.
Conclusion
It’s clear from the above discussion that Japan has become an advanced nation not because of showing progress in a single sector. The current status is a combination of several factors. Years of solid planning and implementation of effective policies by the government have catalyzed the progress.




